In the quest for energy efficiency and sustainable living, HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems play a crucial role. These systems are responsible for maintaining optimal indoor temperatures, ensuring comfort, and promoting healthy indoor air quality.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of HVAC systems, exploring their importance, components, types, energy-efficient features, and maintenance tips. Join us as we uncover the secrets to achieving efficient heating and cooling for a sustainable and comfortable home.
1. Understanding the Importance of HVAC Systems:
1.1 Indoor Comfort: HVAC systems provide the ability to regulate and control indoor temperatures, ensuring comfort regardless of the external weather conditions.
1.2 Energy Consumption: Heating and cooling account for a significant portion of household energy consumption. Efficient HVAC systems minimize energy usage, resulting in reduced utility bills and environmental impact.
1.3 Indoor Air Quality: HVAC systems contribute to maintaining healthy indoor air quality by circulating and filtering the air, removing pollutants, dust, and allergens.
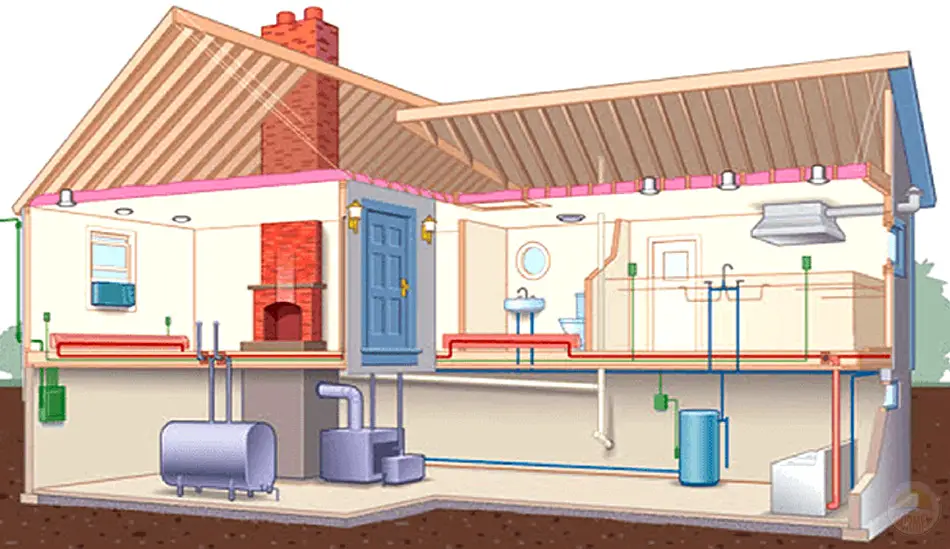
2. Components of HVAC Systems:
2.1 Furnace/Boiler: Responsible for heating the air or water used in the system, furnaces or boilers can run on various fuel sources such as natural gas, oil, or electricity.
2.2 Air Conditioner/Heat Pump: These systems provide cooling by removing heat from the indoor air. Air conditioners use refrigerants, while heat pumps can also reverse their operation to provide heating during colder seasons.
2.3 Ductwork: Ducts are used to distribute heated or cooled air throughout the building. Properly sealed and insulated ductwork ensures efficient airflow and minimizes energy loss.
2.4 Thermostat: The control center of the HVAC system, the thermostat allows users to set and maintain desired temperatures. Smart thermostats provide advanced features like programmable schedules and remote control.
3. Types of HVAC Systems:
3.1 Split Systems: The most common type, split systems consist of an outdoor unit housing the condenser and compressor, and an indoor unit containing the evaporator coil and air handler. They are suitable for both heating and cooling.
3.2 Packaged Systems: In packaged systems, all components, including the condenser, compressor, and evaporator, are housed in a single outdoor unit. These systems are ideal for smaller spaces and require less installation space.
3.3 Ductless Mini-Split Systems: Ductless systems are versatile and offer zoned heating and cooling. They consist of an outdoor unit and individual indoor units, allowing for customized comfort in different areas of the building.
4. Energy-Efficient Features:
4.1 ENERGY STAR Certification: Look for HVAC systems with the ENERGY STAR label, indicating compliance with energy efficiency standards. These systems can significantly reduce energy consumption and deliver substantial savings over time.
4.2 High Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) Rating: SEER ratings indicate the cooling efficiency of air conditioners. Higher SEER ratings signify greater energy efficiency.
4.3 Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) Rating: AFUE ratings measure the heating efficiency of furnaces or boilers. Opt for systems with higher AFUE ratings for increased energy savings.
4.4 Variable-Speed Motors: HVAC systems equipped with variable-speed motors adjust their operation to match the specific heating or cooling needs, resulting in reduced energy usage and enhanced comfort.
4.5 Programmable Thermostats: Install programmable or smart thermostats to set temperature schedules, allowing for efficient temperature control and energy savings by adjusting settings based on occupancy patterns.
5. Maintenance and Efficiency Tips:
5.1 Regular Filter Replacement: Clean or replace air filters at recommended intervals to ensure efficient airflow and maintain optimal system performance.
5.2 Proper System Cleaning: Schedule professional HVAC maintenance to clean system components, remove debris, and optimize system efficiency.
5.3 Ductwork Inspection: Periodically inspect ductwork for leaks, damage, or insulation issues, as leaks can lead to energy loss and reduced system efficiency.
5.4 Airflow Optimization: Ensure that vents and registers are unobstructed by furniture or other items, allowing for unrestricted airflow and even temperature distribution.
5.5 Seasonal Check-ups: Schedule seasonal maintenance visits to assess system performance, identify potential issues, and optimize efficiency before the peak seasons.
Efficient heating and cooling through HVAC systems is essential for creating a comfortable and sustainable living environment. By understanding the components, types, energy-efficient features, and maintenance requirements of HVAC systems, you can make informed choices to reduce energy consumption, lower utility bills, and contribute to a greener future. Embrace the power of HVAC systems for efficient heating and cooling, and enjoy the perfect balance of comfort and sustainability in your home.

